Non-Reflective Boundary Conditions for CAA
Ryu Fattah and James Gill
Last updated on March 24, 2020
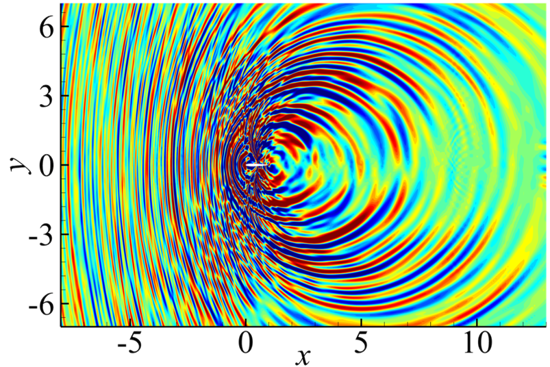
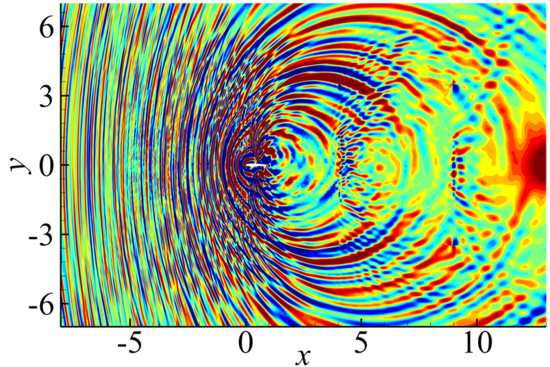
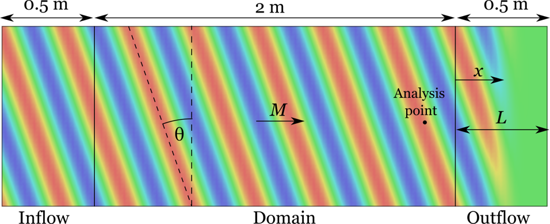
A zonal characteristic boundary condition was developed from two benchmark test cases. The acoustic plane wave tests accurately quantify the reflections generated a boundary condition across a range of Mach number, wave angle, and streamwise and transverse wave numbers. The other benchmark test case used synthetic turbulence to model the vorticity disturbances. Several tests were conducted to evaluate the performance of various methods. The free parameters in the zonal characteristic method were optimized to minimize the acoustic reflections for both acoustic and vortical cases. The final result is a near-perfect non-reflective boundary condition. Finally, the optimal methods from both benchmark cases were blended into a generalized formula
A zonal characteristic boundary condition was developed from two benchmark test cases. The acoustic plane wave tests accurately quantify the reflections generated a boundary condition across a range of Mach number, wave angle, and streamwise and transverse wave numbers. The other benchmark test case used synthetic turbulence to model the vorticity disturbances. Several tests were conducted to evaluate the performance of various methods. The free parameters in the zonal characteristic method were optimized to minimize the acoustic reflections for both acoustic and vortical cases. The final result is a near-perfect non-reflective boundary condition. Finally, the optimal methods from both benchmark cases were blended into a generalized formulation that automatically switches depending on the local vorticity magnitude.